“Inside Iraqi Politics” is a special series dedicated to examining political progress in Iraq, with a focus on issues that affect the country’s stability and the reconciliation between ethnic and religious sects. The series presents a more comprehensive view of factors that slow progress beyond sectarian interest, including the rapid growth of the government, administrative inexperience, corruption, and the structure of the executive and legislative branches outlined in the Iraqi Constitution.
Part 1: Examining the Iraqi executive branch
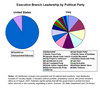
The first installment overviews broad political goals and various influences on progress by the executive branch, including the design of the government under the Iraqi Constitution, Iraqi
administrative experience, rapid growth, and corruption.

|
|
The 275 member Iraqi parliament is divided among a wide variety of political blocs, most of which are in turn composed of various parties. Click image to view. |
Part 2: A look at executive branch progress
The second installment examines the efforts by Iraq’s executive branch to improve services and achieve reconciliation, including an in-depth profile of the Iraqi Implementation and Follow-Up Committee for National Reconciliation and the Baghdad Services Committee, special bodies appointed by Prime Minister Maliki.
Part 3: Examining the Iraqi legislative branch
The third installment examines the structure and political composition of the Iraqi legislative branch, including a review of sectarian distribution and major political blocs within the Council of Representatives.
Part 4. A look at legislative progress: Reconciliation via wealth distribution
The fourth installment begins examination of legislative progress, specifically the status of key legislation that distributes the country’s wealth, including the 2008 budget and the oil law.
Part 5. A look at legislative progress: Sunnis’ and states’ rights
The fifth installment reviews further pieces of legislation considered important for stability and reconciliation: the Unified Retirement Law, de-Baathification reform, the General Amnesty Law, the referendum on Kirkuk, the Provincial Powers Act and the Provincial Elections Law.